To scale a fast-growing SaaS company, your primary focus should be increasing revenue. Seeing all those sales bookings rolling in is very exhilarating; indeed, however, it's easy to forget about what hits the books.
SaaS revenue recognition can be nightmare-inducing for firms using it, because it needs to take into account multiple revenue streams and metrics in order to be calculated successfully. This guide should therefore help you to understand a few of the topline metrics— bookings, billings, and revenue.
What are Bookings in SaaS?
Bookings are the primary indicator of future revenue growth. With the help of bookings, you can measure your increase in sales over a specific period. In short, bookings reflect your customers’ commitment to pay for your services.
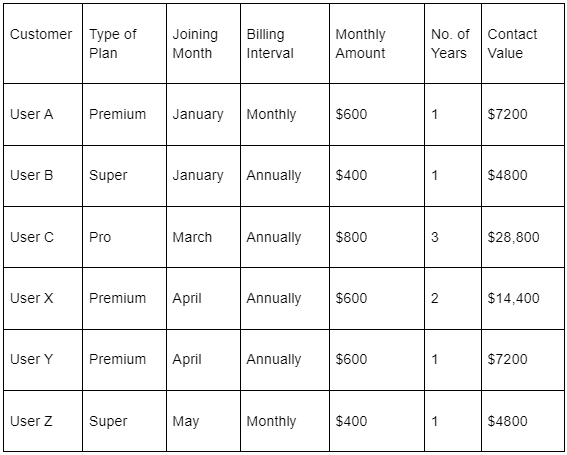
In the example above, User X pays $600 monthly, which equates to $7200 annually. They purchase the plan for two years making their contract value $14400. This would be referred to as a ‘booking’.
Types of SaaS Bookings
The following SaaS bookings are commonly found in the SaaS market:
**1) New Bookings - ** This involves customers/new subscriptions as well as existing users who subscribe to new services
**2) Upgrades or Expansion Bookings - ** These are made up of customers who have decided to expand their contract through upselling expansion services or upgrades
**3) Renewal Bookings - ** This includes existing users who want renewal and are measured either when a renewal request is received or at the renewal date
**4) Non-Recurring Bookings - ** This includes additional one-time fees for products/services like installation, training, and discounts that aren’t a part of the subscription
**5) Annual Contract Value (ACV) Bookings - ** This is the contract value that a customer commits to pay in the first year of a multi-year contract. These ensure a minimum of one year of revenue
**6) Total Contract Value (TCV) Bookings - ** This is the total amount of money the user pays over a multi-year contract.
Why are SaaS Bookings Important?
We already know that SaaS bookings primarily indicate the future revenue growth of the business. Below we’ve listed why bookings in SaaS play a vital role-
1) Derive Insights
You can determine which prospects are most likely to buy into what plan using your customer acquisition and renewal rates. You might also want to use this information to determine who was responsible for winning over new customers — maybe they were able to get an upgrade on their product.
2)Evaluate Sales Success
One of the best ways to evaluate sales success is looking at sales booking data. This metric estimates how much revenue your company has earned, including non-recurring bookings, and it's crucial because MRR doesn't count for these types of charges.
3) Convert Bookings into Recognized Revenue
Improving the effectiveness of your sales bookings and the product delivery is vital for converting them into recognized revenue.
If you find that bookings are high, but revenue recognition rates are low, it could point to an inefficient system that needs improvement or reevaluation entirely.
4) Important Metric for Finance Teams
Bookings prove to be a vital metric for CFOs and finance teams. It helps plan cash outflows and inflows and report bookings as committed money without recording them officially on your revenue stream. This leads to a more accurate calculation of MRR and ARR.
What are Billings?
Billings are an essential metric for any business to track as they are the closest relation to cash flow out of the three metrics.
In layman's terms, it refers when you receive the money from your customers/subscribers. This can happen over a certain period, like- at the time of booking if customers pay in advance, or at the time of revenue recognition if customers pay you in arrears.
Billings are an excellent measure of the health of your SaaS business, because they represent the money that’s owed to you. Using the example shown above, User A is billed for $600 every month in our data set, and this is their billing value.
What is Revenue?
Revenue is the income you earn when your service is delivered successfully to your customers. According to GAAP rules, revenue can only be fully recognized when the customer has received the benefits of what they paid for; it will only happen once it has been 'earned'.
In the case of SaaS, one's core operation is to deliver cloud-based services according to contracts and SLAs.
Compared with bookings which (in a specified period) refer to total value signed over time, revenue guarantees the materialization of specific items based on the client’s demands and contract.
Revenue is a 'gold standard' metric, and investors will look at your revenue when deciding whether to invest in you.
Deferred Revenue Vs Recognized Revenue
1) Recognized Revenue
Recognized revenue is the amount of money you have received from your customers after they've made bookings, and those bookings have been fulfilled according to the contract.
According to GAAP, revenue can only be recognized if the services have been delivered. It can be recognized at once or gradually depending on payment terms.
For instance, a $200payment billed monthly would be recognized entirely within that month, whereas a $2000 payment billed annually would be recognized at a rate of $166.67 each month.
2) Deferred Revenue
If you have a lot of annual billing deals, your company may be experiencing high levels of deferred revenue. This means that even though the money has already been billed and is on account for your products/services, it can’t yet be recognized because they haven't been fully served to their customers yet.
For a few transactions, it’s easy to keep track of deferred and recognized revenue manually, but as your business grows and your number of transactions grow, this can become increasingly difficult. Especially if you offer varying billing lengths.
SaaS bookings Vs billings Vs revenue: Key differences
There are three critical differences between bookings, billings, and revenue for SaaS businesses:
1) Different Portions of Income in Every Period
In SaaS companies, there is a specified period between the contract being signed, the invoice being generated, and the service being delivered.
Thus, although SaaS bookings, billings and revenue sum up to be of the same value by the end of the contract, they might record different amounts each month.
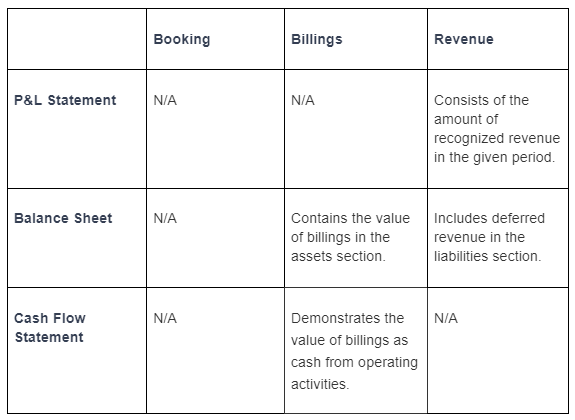
2) Recorded Differently in Financial Statements
there are three vital financial statements- the profits & loss statement, the balance sheet and the cash flow statement. SaaS bookings, billings and revenue affect each of the above statements in different ways:
3) Play Different Roles in Financial Modeling
Bookings and revenue are the foundation of any financial model. Financial models shows how much money you can expect to make in each period based on your current bookings and contracts that haven't yet been signed. It is best to correctly include both in your financial model to understand revenue growth over a long period.
Contrarily, billings are not a part of revenue projection; however, they form a basis of the cash flow projection. You can easily predict when you might receive payments for all your bookings about your billing schedule.
Reporting Bookings, Billings and Revenue
After thoroughly understanding these terms, it's also essential to learn how they are reported in SaaS Accounting.
Bookings don't impact financial or income statements directly because, as mentioned earlier, bookings are not a standard GAAP term but might encourage sales, cash flow and overall business performance.
Billings, on the contrary, affect the balance sheet, which includes deferred revenue, cash balance and accounts receivable, and the income statement, which provides for recognizing revenue over some time.
The revenue recognition standard covered by ASC 606 (GAAP Framework) applies to all sectors and industries. It can be a little more complicated in the SaaS world because of recurring business models. Still, the primary principles remain constant - you only need to understand how your company operates.
Metric Vs Reality
When evaluating data on a multi-year basis, the reality can differ from projected figures. This is because there are many complexities involved in understanding how things work and why one thing happens while another doesn't. This means that businesses need to keep it simple.
They should do this by being consistent and transparent with their reporting practices or else face difficulty explaining these differences between expected outcomes/projections versus actual performance.
When business owners report metrics like bookings, billings, and revenue, they should consider accessing data in the long term to make sure that these numbers are accurately disclosed. It’s also vital to keep in mind, that sometimes more reporting just for the sake of it can also be detrimental.
Clarity and conciseness play an essential role when communicating with investors or other external parties about financial reports. The more explanation there is on what was reported versus how stated beforehand - without unnecessary details, the less are the chances of inquiries on the validity of financial reports.
Simplifying Revenue Recognition
This guide highlights the benefits of regularly tracking SaaS Metrics —bookings, billings and revenue. Recurring Billing is the heart of every SaaS business and requires efficient revenue recognition. So, if you find it a big chore to keep track of all your bookings, billings and revenue, you should consider using Billsby!
Billsby is an easy to integrate subscription billing software that helps manage recurring billing and ascertains globally compliant revenue recognition. With Billsby, you'll have accurate financial metrics that'll allow you to focus on expanding your business.
FAQs
1) How to calculate ACV?
The standard formula for calculating Annual Contract Value (ACV) for a single account is- ACV = Total contract value ÷ Number of years. For instance, if Customer X signs a three-year annual subscription contract with the contract's total value being $1500, the ACV calculation will be: ACV = $1500 ÷ 3 = $500
2) What is the Difference Between Revenue and Income?
Revenue refers to the total amount of income generated by the sale of the company's primary operations. Income refers to the company's total earnings or profit.